
GLP-1 drugs boost health but challenge plastic surgery as rapid weight loss triggers facial sag and skin changes, prompting new options and lifestyle guidance.

Aetna Medicaid and the National Association of Community Health Centers have partnered to reduce high blood pressure rates among Medicaid members in select states by expanding community-based care.

A new economic evaluation finds that pairing extended counseling with a brief course of nicotine replacement therapy offers the best value for health systems integrating smoking cessation into lung cancer screening.
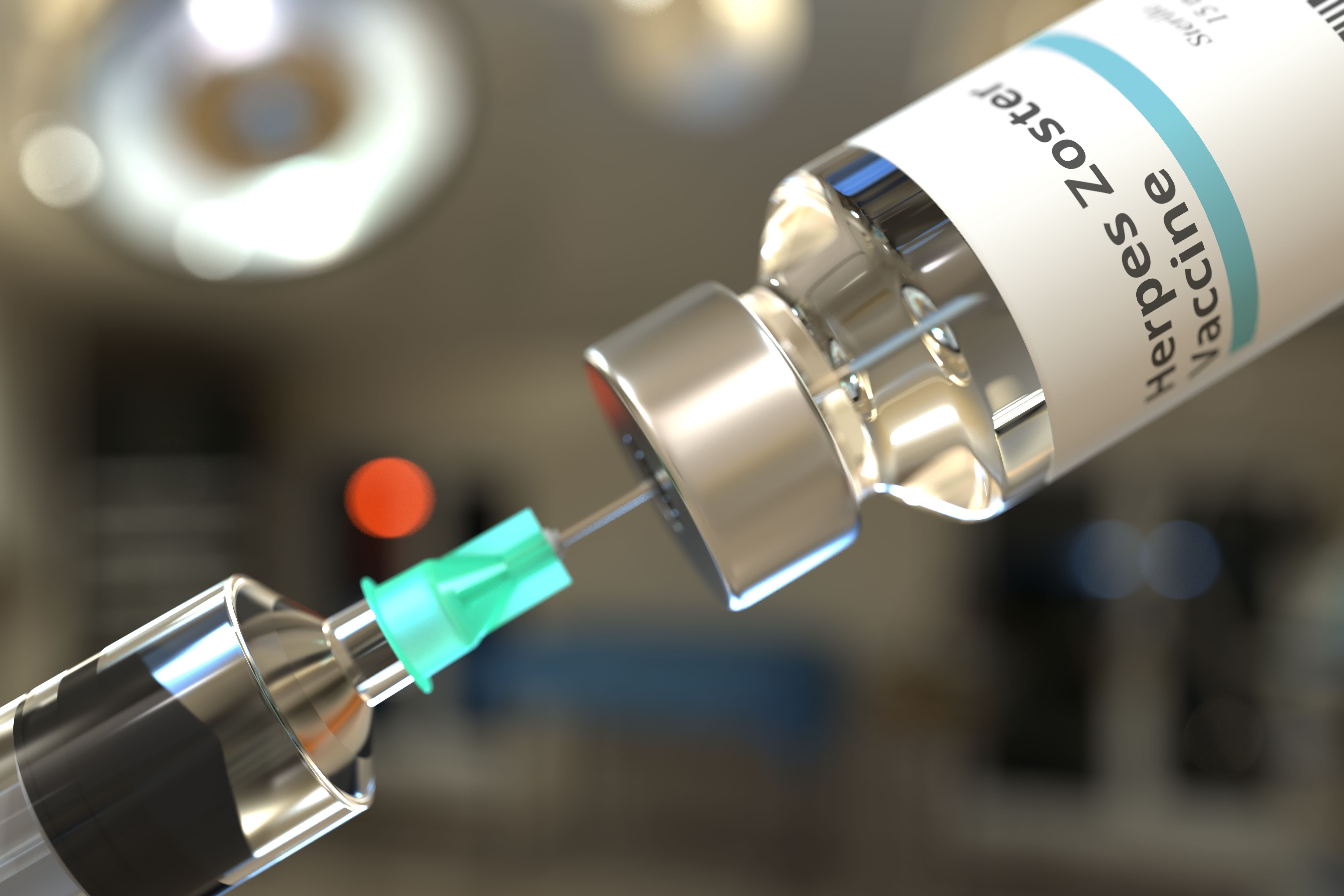
A new study finds that the recombinant zoster vaccine was associated with a 51% lower risk of dementia. This was seen across age and racial and ethnic groups, but the risk reduction was stronger in women compared with men.

A conversation with Gil Yosipovitch, M.D., explores why itch worsens at night, how it rivals chronic pain in quality-of-life impact, and why better assessment of nighttime itch and sleep disruption is urgently needed.

Clinicians weigh sonic sleep tools: who benefits, how to use phone-based audio safely and why CBT-I stays first-line for insomnia.

During an investor call, CVS Health executives said the new legislation requiring changes in PBM business practices was manageable, but they expressed some concern about CMS’s Medicare advanced rate notice.

GLP-1 weight-loss drugs can trigger facial fat loss, deepening wrinkles and sagging; experts warn appearance concerns may reduce adherence and affect health outcomes.

A recent analysis shows that most products subject to price reduction under the Inflation Reduction Act have achieved substantial returns on investment by the time of negotiations.




